5 - Lines parallel to coast
Source:vignettes/5_add_line_parallel_to_coast.Rmd
5_add_line_parallel_to_coast.RmdThis example shows how to make a line that is parallel to the coast and how to make a line that follows the coast but removes any inlets (like Puget Sound or San Francisco Bay).
Load the sample data.
data("sample_raster", package="basics")
df <- sample_raster$df
ras <- sample_raster$raster
lons <- sample_raster$lons
lats <- sample_raster$latsLoad the needed packages for plotting.
## Loading required package: raster## Loading required package: sp## Loading required package: ggplot2Download the world coastlines
For this buffer, I am using a fairly zoomed out version of the coastline. You could use the coastline from rnaturalearth.
Create a line around the world’s coastlines at 300 km offshore
This is a projection in meters (not longlat). Note that I have set the units to km. See comments in the add_coast_buffer vignette about why rgeos::gBuffer() must be used and not raster::buffer().
- Select a project in meters not longlat
- Transform our world polygon in that projection
- Create a buffer polygon around the world polygon
- Erase the interior world polygon (not sure one has to do that but you do)
- Clean up by removing some of the small holes in the buffer polygon
# Step 1
newcrs <- "+proj=wintri +lon_0=0 +lat_1=0 +x_0=0 +y_0=0 +datum=WGS84 +units=km +no_defs"
# Step 2 World coastline in meters
data("world", package="basics")
mworld <- sp::spTransform(world, newcrs)
# Step 3
buff300 <- rgeos::gBuffer(mworld, width = 300, byid=TRUE)
# Step 4
e <-raster::erase(buff300, mworld)We want just the outer part of this polygon. We will use the remove.holes() function from spatialEco.
# Step 5
e300 <- spatialEco::remove.holes(spatialEco::remove.holes(e))## Warning in sp::proj4string(x): CRS object has comment, which is lost in output
## Warning in sp::proj4string(x): CRS object has comment, which is lost in outputNow we can plot and the holes that were removed are the red lines.
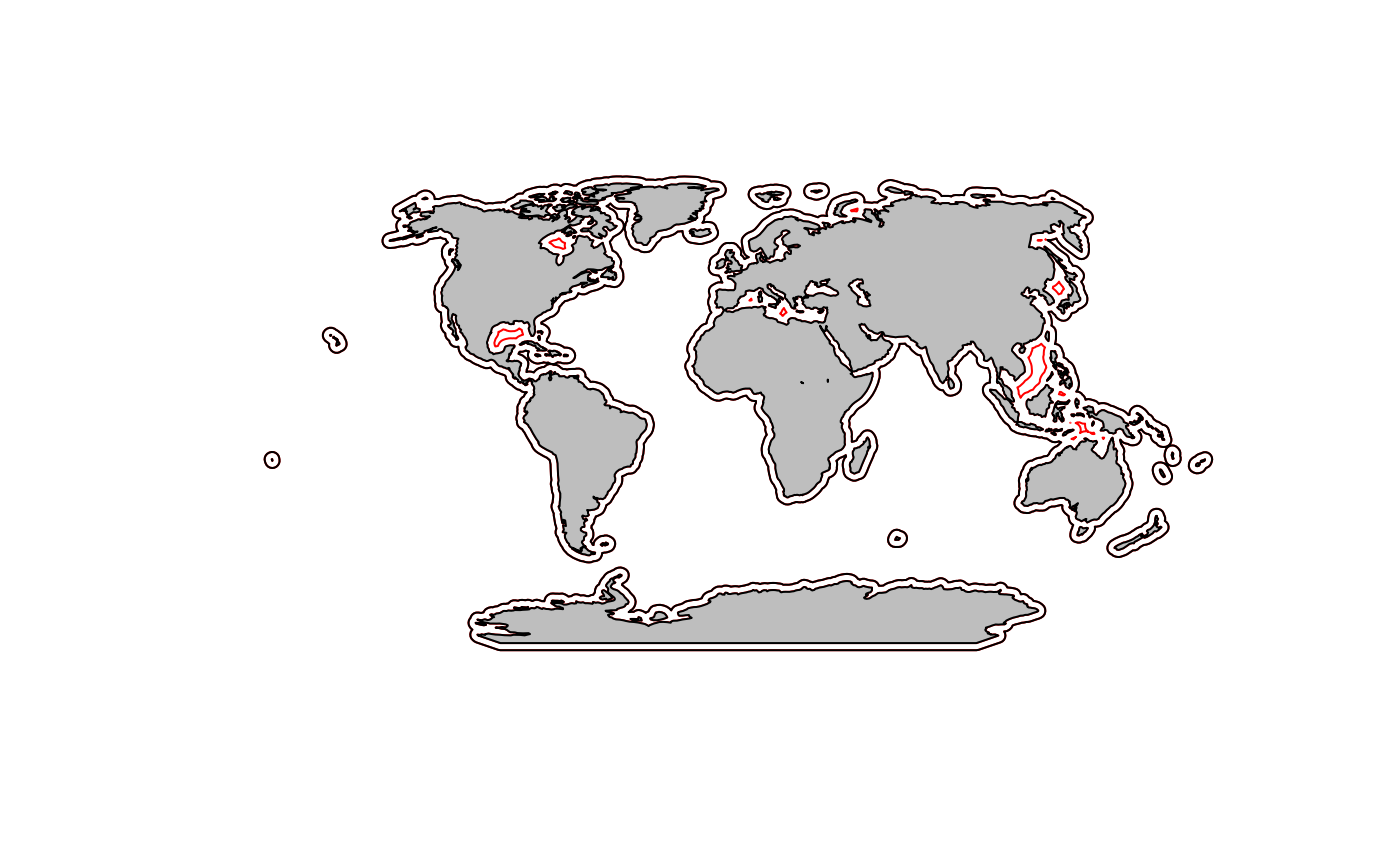
pts <- sp::SpatialPoints(cbind(lons, lats), proj4string = sp::CRS("+proj=longlat"))
mpts <- sp::spTransform(pts, newcrs)
plot(e300, border="red", axes=TRUE, xlim=mpts@bbox[1,], ylim=mpts@bbox[2,])
plot(mworld, add=TRUE, col="grey")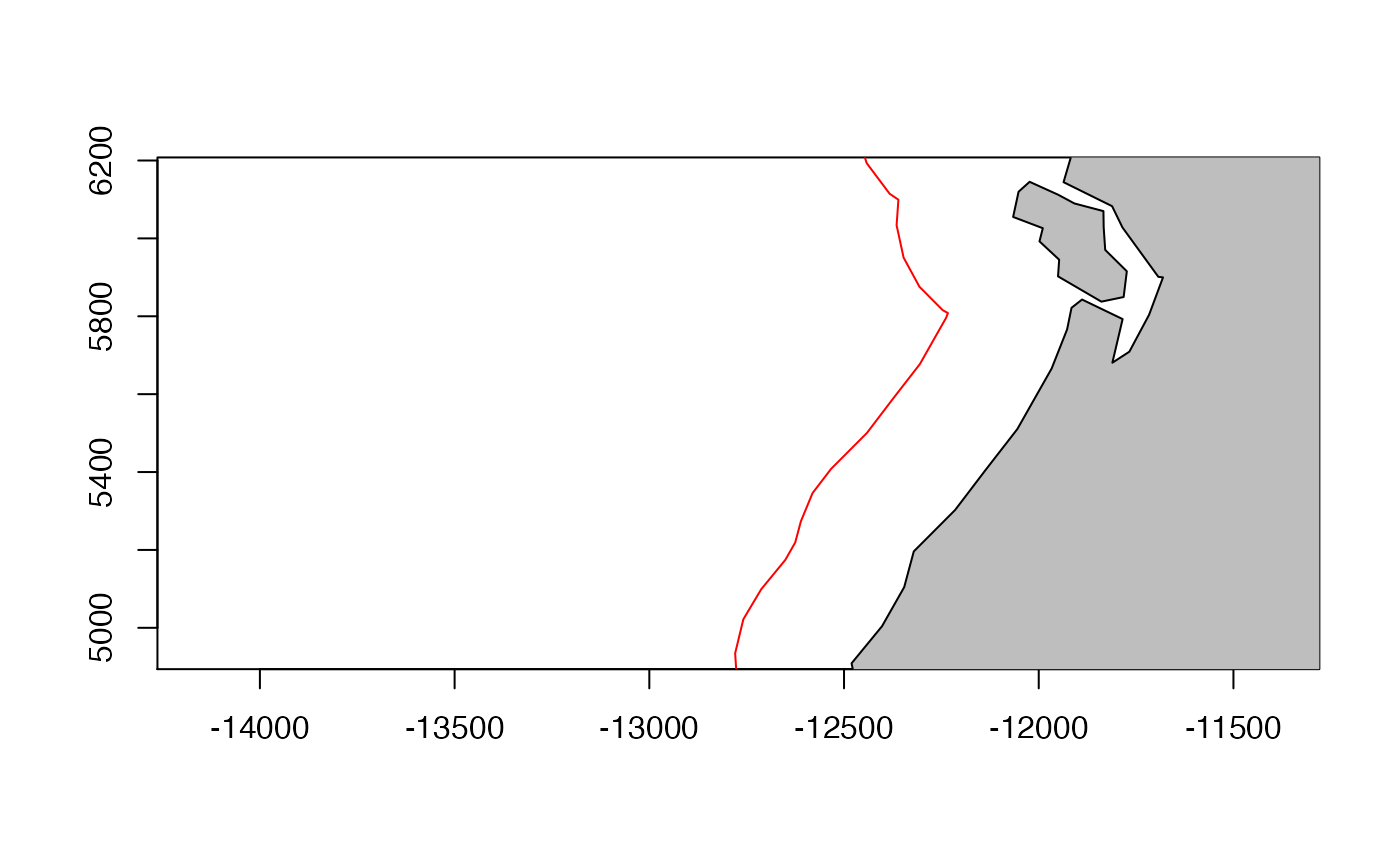
Create a line around the world’s coastlines at 10 km offshore
We could use the method above but the 20 km buffer would dip into the inlets and we don’t want that. We want this to be 280 km inside of the 300km line.
- Turn
e300into lines. Otherwise our 280 km buffer will only be outside and we want the inner one. - Create a 290 km buffer to that
- Keep ONLY the holes on that new buffer object.
el300 <- as(e300, "SpatialLines")
buff20 <- rgeos::gBuffer(el300, width=280)If we plot this we see that it is on both sides of our 300 km line. We want only the inner lines.
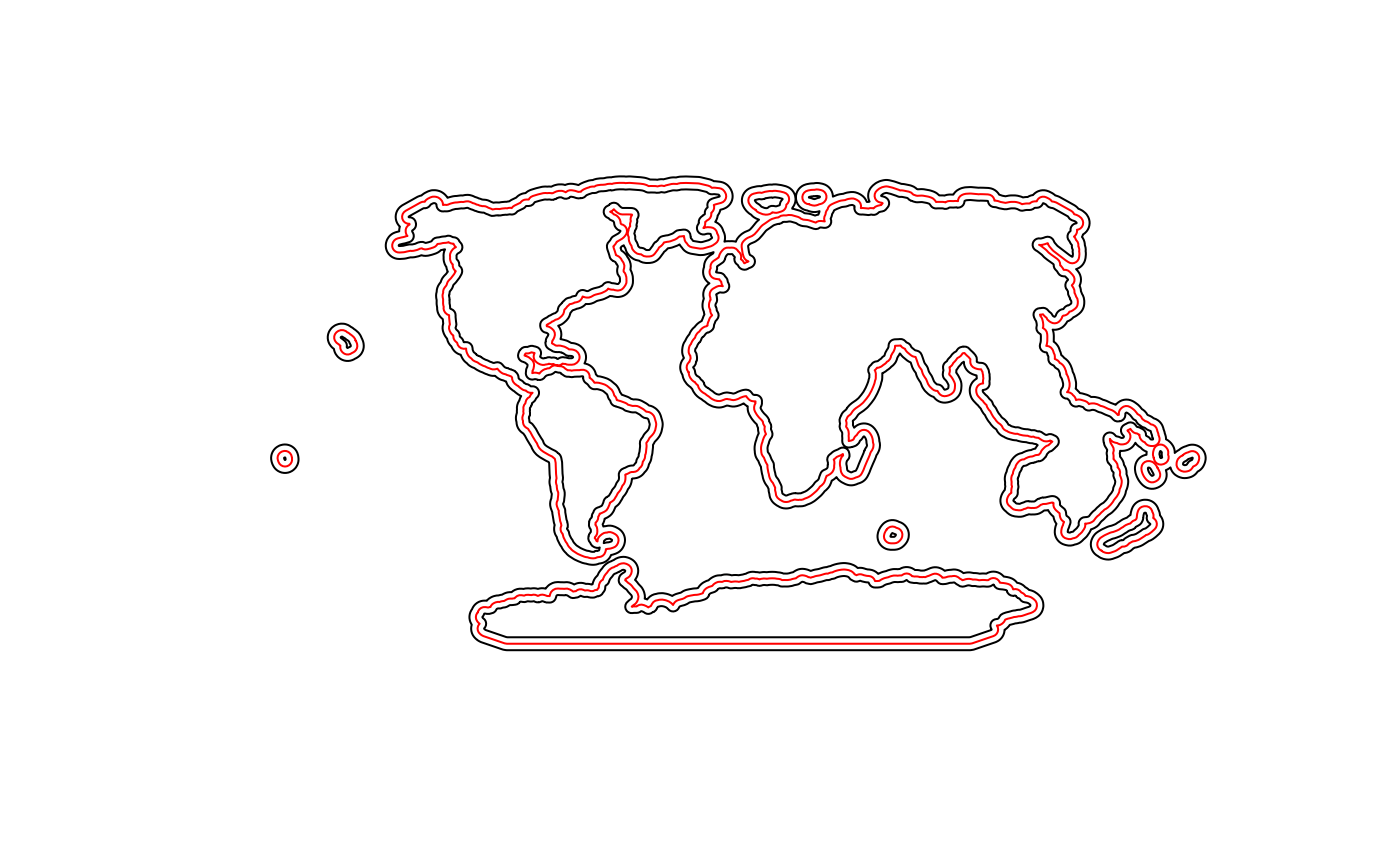
Remove the outer part of the polygons. Let’s make it lines too.
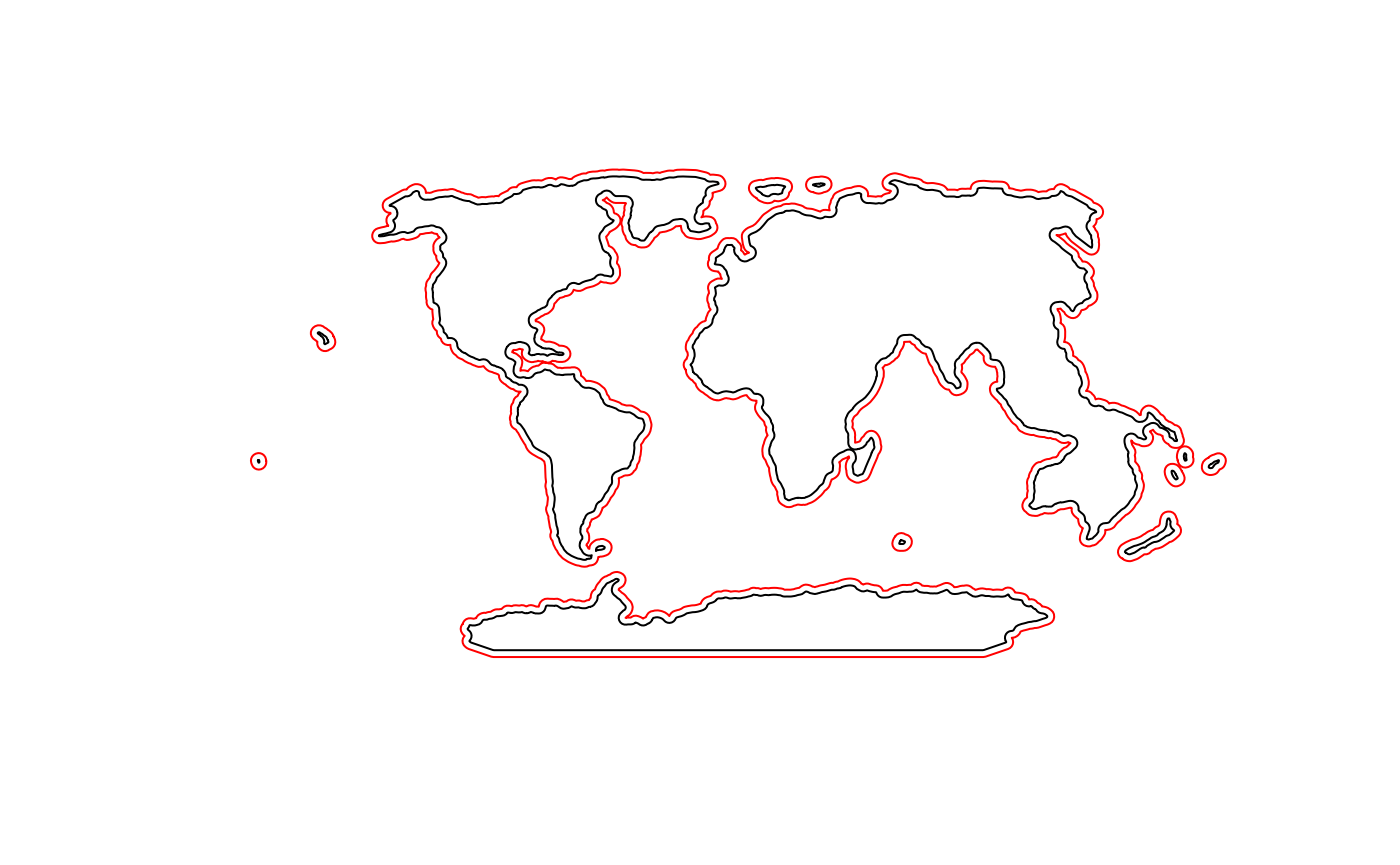
e20 <- only.holes(buff20)## Warning in sp::proj4string(x): CRS object has comment, which is lost in output
el20 <- as(e20, "SpatialLines")Now it looks better. Potentially we’ll want to remove the smaller polygons (islands).
We can look off the WA coast.
plot(el20, col="black", axes=TRUE, xlim=mpts@bbox[1,], ylim=mpts@bbox[2,])
plot(el300, add=TRUE, col="red")
plot(mworld, add=TRUE, col="grey")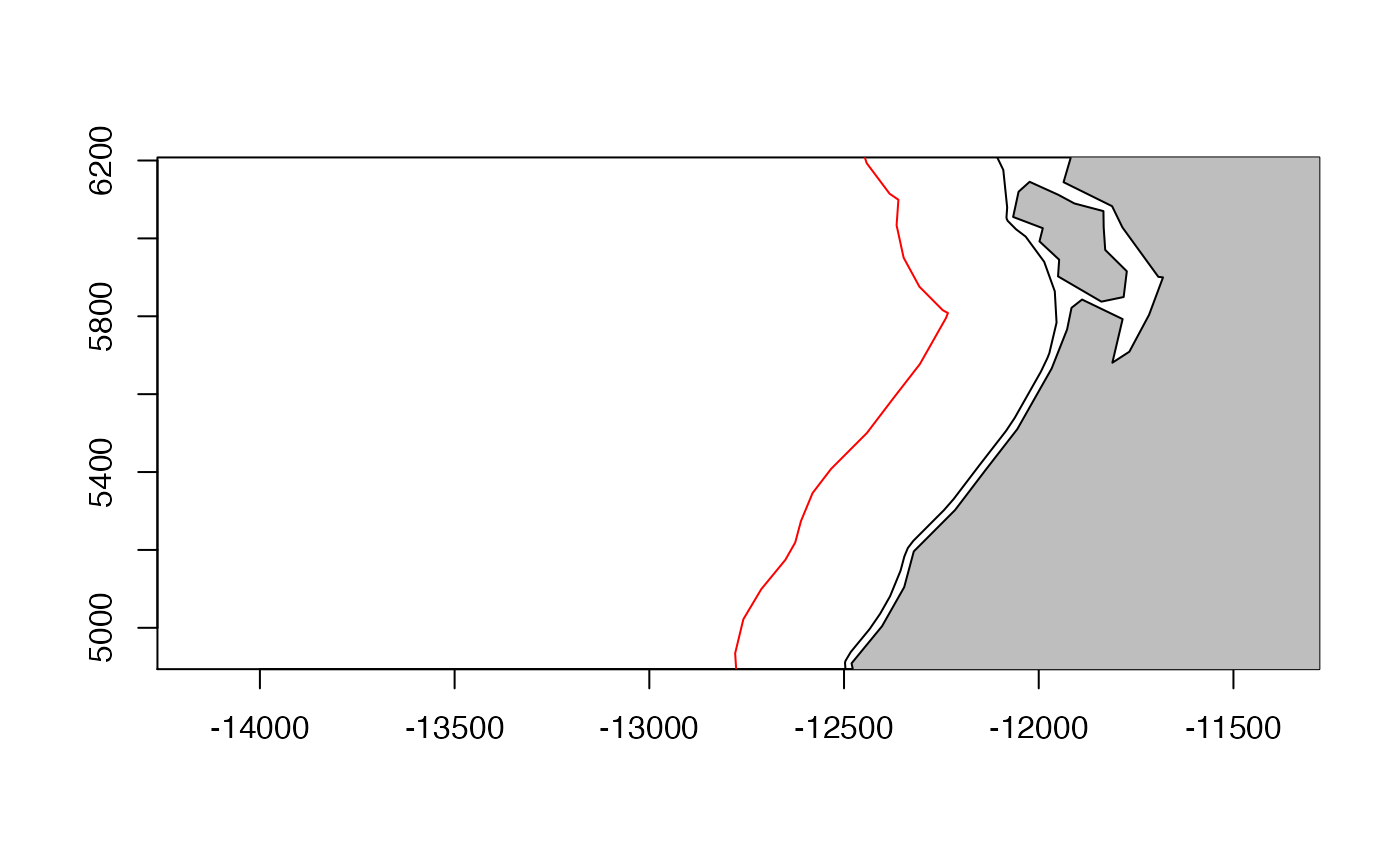
Add sample locations
Now we can add some locations where we will sample the coastline
numOfPoints <- rgeos::gLength(el20) / 100
sample.pts <- sp::spsample(el20, n = numOfPoints, type = "regular")
plot(el20, col="black", axes=TRUE, xlim=mpts@bbox[1,], ylim=mpts@bbox[2,])
plot(el300, add=TRUE, col="red")
plot(mworld, add=TRUE, col="grey")
plot(sample.pts, add=TRUE, pch=1)
title("sample points every 100 km")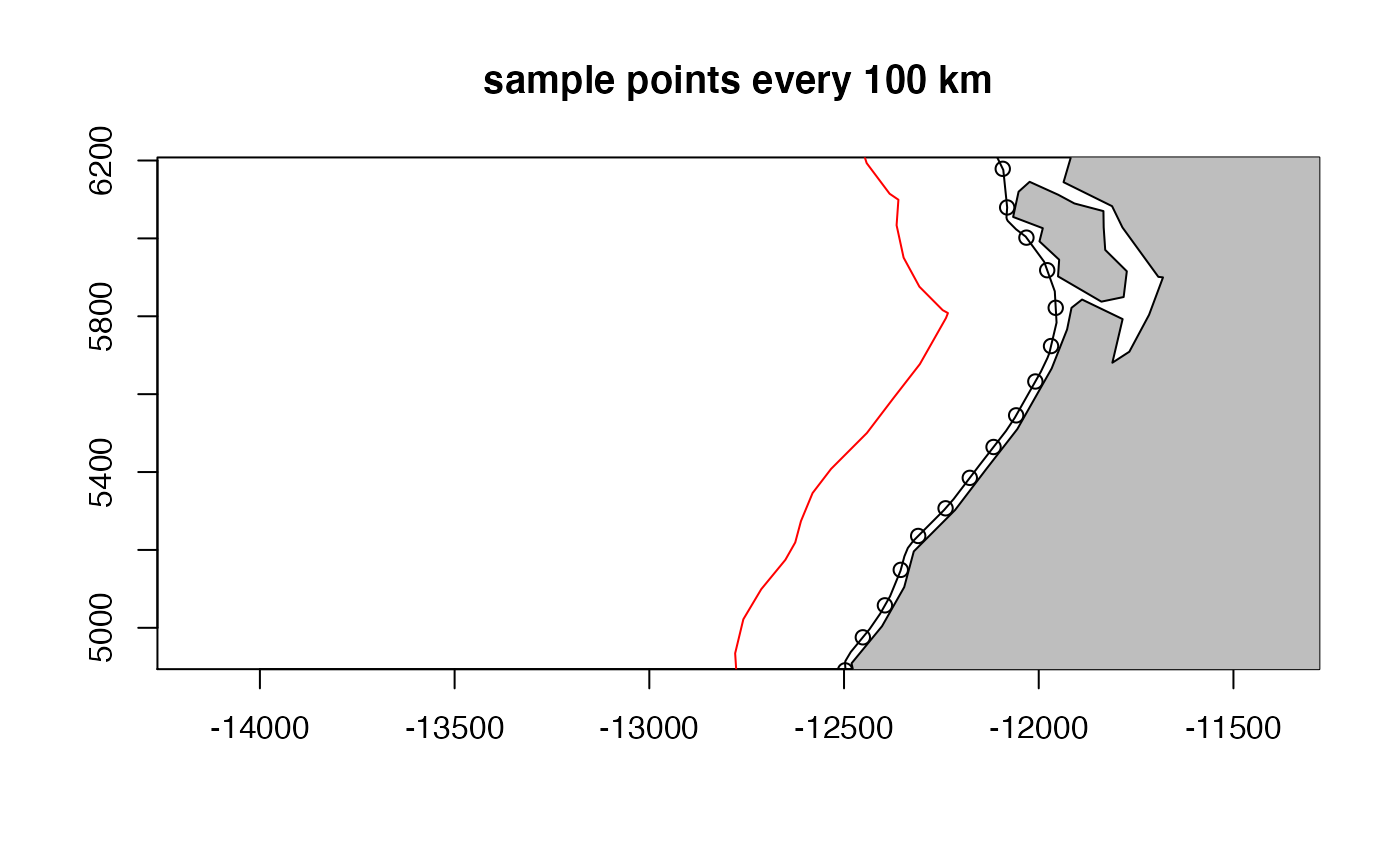
Only Holes function direct from spatialEco::remove.holes()
only.holes <- function (x)
{
if (!any(which(utils::installed.packages()[, 1] %in% "maptools")))
stop("please install maptools package before running this function")
xp <- slot(x, "polygons")
holes <- lapply(xp, function(x) sapply(methods::slot(x, "Polygons"),
methods::slot, "hole"))
res <- lapply(1:length(xp), function(i) methods::slot(xp[[i]],
"Polygons")[holes[[i]]])
IDs <- row.names(x)
x.fill <- sp::SpatialPolygons(lapply(1:length(res), function(i) sp::Polygons(res[[i]],
ID = IDs[i])), proj4string = sp::CRS(sp::proj4string(x)))
methods::slot(x.fill, "polygons") <- lapply(methods::slot(x.fill,
"polygons"), maptools::checkPolygonsHoles)
methods::slot(x.fill, "polygons") <- lapply(methods::slot(x.fill,
"polygons"), "comment<-", NULL)
pids <- sapply(methods::slot(x.fill, "polygons"), function(x) methods::slot(x, "ID"))
x.fill <- sp::SpatialPolygonsDataFrame(x.fill, data.frame(row.names = pids,
ID = 1:length(pids)))
return(x.fill)
}